The safety seat can't be omnipotent, but it doesn't work without it.
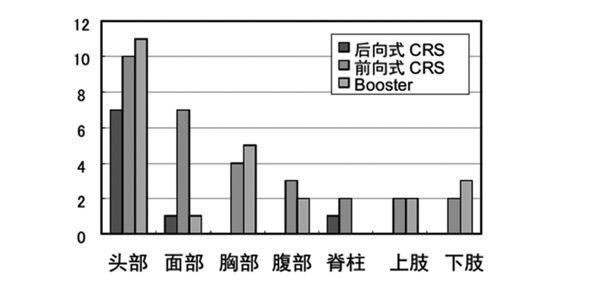
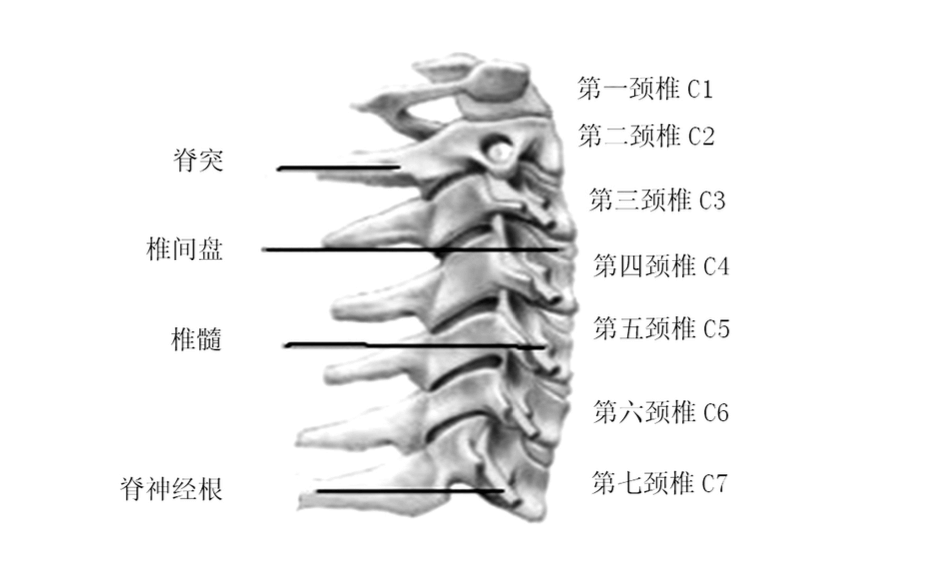
   According to the China Consumer News (Reporter Li Fang ), children as a special group of road users are more vulnerable to serious injuries in road traffic accidents than adults. At the same time, road traffic accidents play a very important role in causing injury or death to children. However, this painful fact is not known to the Chinese people, resulting in many families in the state of "ignorance and fearlessness." On May 27th, the Child Safety Ride Work Promotion Office (CPSPO) publicly disclosed the trauma characteristics of children in traffic accidents for the first time. The brutality of the disclosed car accidents will make many parents understand the meaning of the word "awe". Children's body is fragile and hard to imagine Experts from the China Automotive Technology and Research Center's Child Safety Ride Promotion Office introduced to the China Consumer News reporters the use of the "damage biomechanics" principle method to analyze the situation of children in traffic accidents. Damage biomechanics, also known as collision biomechanics, is an important theoretical basis for human protection in the field of passive safety in automobiles. At present, due to the lack of biomechanical test data for children, researchers generally study and numerically analyze the damage mechanism of children's occupants by scaling the data and models of adults. However, there are significant differences in biomechanical data between children and adults. The above experts believe that based on the statistics of motor vehicle traffic accidents and the biomechanics of child occupant injury, the characteristics of child occupant accident damage and the protective performance of child safety seat are studied. The conclusion is that children are not a miniature version of the adult, not only in the body. In proportion, there are bone structures and material properties. In the accident, the damage mechanism and tolerance limit of the child occupant are also different from those of adults. Whether in a frontal collision or a side collision, the child's occupant is most often injured. Therefore, how to prevent the head forward displacement and lateral displacement from being too large has become the focus of designing child safety seats. Different collisions Experts from the Child Safety Trip Promotion Office told reporters that according to the Volve Insurance Company's traffic accident database, the traffic accidents in Sweden between 1976 and 1996 recorded a collision with children occupants (4242 children aged 0-15). The statistical results of the type show that the frontal collision has the highest probability; the second is the side collision. Among them, the part where the child occupant is injured in the frontal collision is the head, the face and the neck. The cause of head and face injuries is mostly that the forward displacement of the child relative to the seat during the collision process is too large, resulting in a secondary collision with the front seat. However, angular acceleration can cause diffuse brain damage regardless of whether the head is in contact with the internal structure of the vehicle. The neck injury frequency is lower than the head injury, but once it occurs, it is a very serious injury. For child seats with a five-point seat belt restraint, the restraint is the clavicle and thorax on the left and right sides of the child occupant. Since the child's head mass accounts for a large proportion of his body weight, the forward movement of the head can strain the neck. Because the child's neck is soft and not easy to fracture, there will be cases where the cervical vertebrae are not damaged and the cervical cord is injured. Under normal circumstances, chest and abdomen injuries are less likely to occur, and upper and lower limb injuries are generally not fatal. Side impact, the nature of the damage will be more serious. The probability of a side collision of the vehicle is relatively low compared to the frontal collision; however, the serious injury rate of the child in a side collision accident is high. In a side impact accident, the injured part of the rearward child restraint system is mostly the head and face. Child occupant injury site statistics Partial injury According to experts from the Child Safety Carriage Promotion Office, children's bones are not fully calcified, and their elastic modulus and flexural strength are lower than those of adults, but they can absorb relatively large impact energy. An experiment with live piglet replacement showed that in the guard-type seat test, although there were no rib fractures, lung contusions and liver tears were found during the piglet necropsy. This suggests that children's ribs may not have good support for their internal organs. In the five-point seat belt test, all the piglets survived and no chest and abdominal injuries were found. However, blood clots were found in the spinal cord under the dura mater, and about 64.7% of the piglets were exposed to this damage, indicating that the child safety seat does not provide good protection for the child's neck. The ratio of the height of the center of gravity of the head of the child's head and its height is greater than adults. In the event of a positive accident, the child will move forward under the action of inertia. Since the child's torso is restrained by the Child Restraint System (CRS), the forward movement distance is small, but the amount of forward tilt of the head is large, which is easy to follow. There is a secondary collision in the interior parts of the car. Even if there is no impact, the angular acceleration of the center of gravity of the child's head and the diffuse damage caused to the brain cannot be ignored. Secondary collisions often cause bruises, contusions, comminuted fractures, concussions, etc., and the moment of inertia of the head and neck can cause soft tissue damage. The picture of the neck shows seven cervical vertebrae. Among them, the C1-C3 cervical vertebra can be completely combined when the child is 10 years old, and begins to localize at the age of 12, and matures when it is adult. Children's cervical vertebrae are soft and prone to dislocation even under small forces. In the collision, the cervical spine of the infant will have a large deformation and stretch the spinal cord, causing spinal cord injury. Relevant statistics show that nearly 70% of the children's neck is easy to break in the C1 or C2 parts, and the probability of adults breaking in this part is only 16%. This is because the adult's neck pivot is at C6, but the child's neck pivot is at C2 or C3. The ribs of the chest of a child's chest are softer and more tough than adults. Therefore, children are more prone to large deformation rather than fracture when subjected to impact, so the organs in the thoracic cavity are more likely to be injured. In the frontal collision, the child's chest under the restraint of the forward CRS will be restrained by the five-point seat belt, which will easily cause the internal organs to be squeezed, and the rear mounted CRS will protect the chest organs more than the forward installation. Good. Therefore, experts recommend to parents that the child safety seat should be installed in a backward direction. Abdomen Children's abdomen is more bulging and the abdominal muscles are underdeveloped. When a vehicle collision occurs, the belt distributes a part of the impact force to the abdomen area of ​​the child's bulge, which easily causes damage to internal organs, and even gastric perforation, and the mortality after injury is high. According to European statistics, children aged 4-10 years are mainly in the abdomen; in all types of injuries, the proportion of abdominal injuries is 26%. After the 10-year-olds in the pelvis, anterior superior iliac spine, pelvis mature. During the collision, the belt belt can be prevented from sliding to the abdomen. Children under the age of 10, because the anterior superior iliac spine is not fully developed, can not accurately locate the belt belt, it is easy to cause children to dive, so that the belt slides to the abdomen. The interior of the child's pelvis is soft, and the pelvis begins its first ossification when it is about 8 years old. Therefore, children under 8 years of age have fewer pelvic fractures; children over 12 years old and adults are more likely to have pubic fractures. Safety seat new topic It is well known that the use of child safety seats can reduce the death rate of 70% of traffic accidents. However, from the above analysis, even if a safety seat is used, the injury situation cannot be completely avoided. As you know, there is a considerable gap between real car accidents and data modeling under laboratory conditions. The real car accident is even more cruel. The speed limit of domestic highways can not be lower than 70km/h, which is 50km faster than the laboratory test speed. Once a high-speed impact occurs, the chest acceleration, whether it exceeds the 55g limit, is the answer that everyone knows, and the probability of child damage will show a geometric progression. Therefore, experts suggest that choosing a child safety seat with the lowest collision damage value should be an important solution to reduce child injury. The so-called "collision damage value", that is, when a car accident occurs, the safety seat can reduce the degree of damage to children. Experts suggest that in the collision damage value of the child seat, the chest synthetic acceleration is the most important indicator of safety evaluation. The standard for the European standard test is that when the car is subjected to the collision test at a speed of 50 km/h, the chest synthetic acceleration lasting more than 3 ms, which is within 55 g, is acceptable. When the chest synthetic acceleration value is greater than 55g, the human body is unbearable. There is a relatively intuitive metaphor, 30g of gravity acceleration, equivalent to a car, with a speed of 50 kilometers per hour, through a 200mm deep pit, feeling a slight discomfort; when passing through a 500mm deep pit, what feels, can be free Imagine. Therefore, the lower the chest composite acceleration value and the smaller the damage value, the safer the child. At present, most of the domestic safety seat brands, more publicity focus on the appearance, certification and installation and use, but rarely see the brand to do the safety of the seat damage value and dummy head displacement and Promotion. These two indicators are the key to measuring safety indicators for safety seats. How to reduce the value of car accident damage should be a new issue that parents who care about children's safe travel must consider. Related Links Use a safety seat to greatly reduce injuries Motor vehicle traffic accidents are an important factor in causing child casualties. According to the World Health Organization's 2008 Report on the Prevention of Child Injury, more than 2,000 families worldwide lose their children due to road traffic accidents. Between 2012 and 2013, 1,168 and 759 children under the age of 14 (including 14) in the United States and Europe died of road traffic accidents. According to the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, the number of deaths among children aged 1-4 in Japan was 949 in 2008, and the deaths caused by accidents accounted for the largest proportion, reaching 17.1%. The proportion of accidental deaths caused by traffic accidents was 28.2%. In 1971, the United States enforced child safety regulations. From 1975 to 2008, the child restraint system saved at least 8959 children. In 2008, the number of children under the age of 14 who died in a car accident fell to 1,347. With the increase of car ownership and the number of motorists in China, the formulation and enforcement of relevant national laws and regulations, the safety of children's occupants has received more and more attention. Incorrect use of the safety seat is a serious phenomenon China's research on the child restraint system is in its infancy, the child seat usage rate is still very low, and there is a relatively high misuse rate. Zhang Jinchang and other scholars from Tsinghua University conducted a questionnaire survey on parents of children aged 1-6 in Beijing in response to the misuse of child safety seats in China. Mistakes in the questionnaire included five installations: wrong position, three-point adult seat belt slack and twist, five-point seat belt slack and twisting for child occupants. In the final sample of the survey, 52.9% of child safety seats and three-point vehicle seat belts were used, of which 28.6% were used for child safety seats. Among those who used child safety seats, 63.8% were confident that they were installed correctly; but among those who were confident in installing them, only 29.5% were correctly installed. Therefore, combined with the characteristics of children in China and the actual situation of the ride, the damage mechanism of the child occupants and the protective performance of the child seat are studied. The CRS with beautiful design, convenience and low misuse rate improves the safety performance of the child seat and the child occupant. The safety protection is of great significance. Studies have shown that in traffic accidents, the correct use of child restraint systems can reduce mortality by 71% for children under 1 year of age; for children aged 1-4 years, proper use of child restraint systems can reduce mortality by 54%. ( Xiangyang )
A wooden crate has a self-supporting structure, with or without sheathing. For a wooden container to be a crate, all six of its sides must be put in place to result in the rated strength of the container. Crates are distinct from wooden boxes. The strength of a Wooden Box is rated based on the weight it can carry before the top (top, ends, and sides) is installed, whereas the strength of a crate is rated with the top in place. In general conversation, the term crate is sometimes used to denote a wooden box.
Although the definition of a wooden crate, as compared to a wooden box, is clear, construction of the two often results in a container that is not clearly a crate or a box. Both wooden crates and wooden boxes are constructed to contain unique items, the design of either a crate or box may use principles from both. In this case, the container will typically be defined by how the edges and corners of the container are constructed. If the sheathing (either plywood or lumber) can be removed, and a framed structure will remain standing, the container would likely be termed a crate. If removal of the sheathing results in no way of fastening the lumber around the edges of the container, the container would likely be termed a wooden box.
Wood Crate,Rustic Wood Crate,Customized Wood Crate,Wooden Wine Crate Jinan Tri-Tiger Technology Development Co., Ltd , https://www.tigerwoodproduct.com