Screen-printing ink commonly used solvents (2)
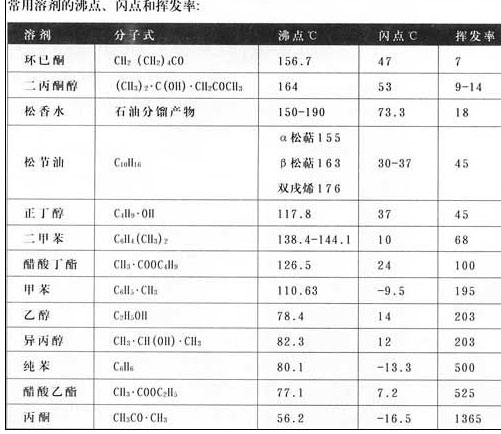
Third, the boiling point, flash point and auto-ignition point of the solvent Organic solvents are flammable (except chlorinated hydrocarbons), and some flash points can reach -16.5°C, so the air circulation must be guaranteed during printing. For safety reasons, no open flame is allowed in the printing shop. 1, boiling point: The boiling point of the solvent is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the solvent reaches one atmosphere. The relative high and low vapor pressures of various solvents at high temperatures are not the same as those at room temperature. 2, flash point: When the solvent is heated, the vapor is emitted into the air. As the temperature rises, the concentration of the solvent vapor gradually increases. When the flame is met, there is a flame, and the temperature immediately goes out. 3, the evaporation rate: At a certain temperature and relative humidity, observe the volatilization rate of a drop of the tested solvent on the filter paper in a box of the specified size and shape. Volatile rate value = butyl acetate volatilization time / volatilization time of tested solvent × 100% The smaller the value of the evaporation rate, the slower the volatilization rate of the solvent, the greater the value of the volatilization rate, the higher the volatilization rate of the solvent. With the help of the following table, in the case of screen printing, especially when the "solvent-evolving ink" is selected, it is possible to select the solvent for the climate season. (See the table below) Fourth, introduce several common solvents 1, pine perfume: Namely, 200# solvent gasoline, which is a product of petroleum separation, can dissolve rosin, glycerin stearate and alkyd resin, and can adjust metal and glass inks. Its solvent power is in the middle range and can be miscible with many organic solvents. 2, turpentine: It is a volatile part of the oil-containing turpentine extracted from pine trees. Turpentine has three isomers: alpha-pinene, beta-pinene, and bis-decene. It evaporates evenly. Due to the unsaturation in the molecular structure, it can produce oxidative polymerization, and it can form a component of film-forming substance that is dissolved in oil and resin. Turpentine oil evaporates evenly and has the effect of preventing crusting and improving leveling properties of oxidized polymeric inks. 3, xylene: Industrial xylene is a mixture of three different kinds of ortho, meta, and para positions. Xylene has a higher dissolving power than turpentine and pine perfume, and the volatilization rate is faster than both. It is widely used in high-temperature curable inks and oxidative polymerization inks. 4, toluene: It comes from the petrochemical or coal coke industry, toluene can dissolve ethyl cellulose, maleic anhydride resin, rubber, vinyl chloride, etc., can adjust the glass ink, metal ink. 5, ethanol: According to different uses, its purity is different, the purity of absolute ethanol is 99.5%, industrial ethanol is 95.6%, and pharmaceutical ethanol is 70~75%. Ethanol can dissolve many natural resins, such as: shellac, polyvinyl acetate, cyclohexanone resin, polyvinyl acetal resin (net-printing plate is used to make it with adhesive mesh), but the sensitivity of ethanol to solvent resistance Destructive effect of glue. 6, diacetone alcohol: The main product that is easily decomposed and decomposed is acetone, which can dissolve rosin, polyvinyl acetate, nitrocellulose, shellac, and chloroacetate copolymer resins. 7, acetone: It is an extremely volatile organic liquid that can dissolve vinyl chloride resin, vinyl chloride vinegar copolymer resin, chlorinated rubber and so on. It has a destructive effect on solvent-resistant emulsion film. However, it is a good solvent for tackifiers. 8, cyclohexanone: Has very good solubility, in addition to some of the natural resin can be dissolved, many of the synthetic resin can be dissolved, and can be miscible with the vast majority of organic solvents, solvent solvent is a good solvent ink. 9, methyl ethyl ketone: It is similar to acetone, but it has a higher flash point and slower evaporation rate. It is soluble in water, ethanol, ether and hydrocarbons and oils. 10, isopropyl alcohol: It is soluble in water, ethanol, ether and chloroform. 11, butanol: It can dissolve many natural resins and synthetic resins, such as polyvinyl acetate resin, melamine resin, etc. Butanol and xylene can be used for high temperature curing inks and epoxy inks in a ratio of 3:7. Ethyl acetate: It can dissolve ethyl cellulose, nitrocellulose, chlorided cypress, chloroacetate copolymer resin and so on. 13, butyl acetate: It can dissolve many synthetic resins, such as polyvinyl chloride resin, chloroacetic copolymer resin, chlorinated rubber, polyvinyl chloride resin, etc. It is a solvent for solvent evaporation type ink, but it is not suitable for use in summer printing because of its quick volatilization. 14, kerosene: Also known as flame oil, a colorless or light yellow transparent oily liquid, is a petroleum distribution product that can be used to produce printing paste. Five, note the solvent with ink transfer 1. The solvent used for ink transfer should have good mutual solubility with the polymer resin in the ink. 2. The volatilization rate of the solvent used should be uniformly decreased with the drying of the ink layer to prevent the surface of the ink film from being morbid. 3, organic solvents are flammable, and have a certain toxins on the human body, so it is necessary to maintain the printing shop air circulation, and avoid the existence of fire. Source: 21st Century Fine Chemicals Network Pet Supplies,Outdoor Dog House,Wooden Dog House,Multi-Level Tall Cat Condo Furniture HANGZHOU JIEYUN IMP & EXP CO., LTD , https://www.jaalex-garden.com